Germinating plant seeds is the process by which a seed transforms into a sprout and eventually a full-grown plant. It is a crucial step in plant growth and reproduction, and understanding the factors that affect the germination of small seeds can greatly improve your success in gardening and farming. This ultimate guide to seed germination provides a comprehensive overview of everything you need to know about the process, including the different types of seeds, the factors that affect germination, and the methods used to initiate germination. Whether you are a beginner gardener or a seasoned professional, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and skills necessary to successfully germinate seeds and grow seedlings healthy, thriving plants.
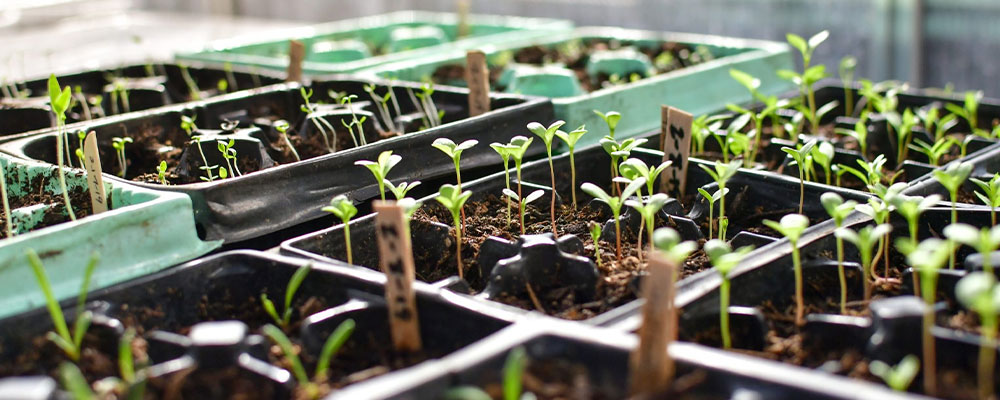

The Importance of Getting Seeds Germination

Getting seeds to germinate successfully is an essential aspect of gardening and farming. Without successful germination, plants cannot grow and produce the food, flowers, or foliage that we desire. Germinating seeds is the starting point for plant growth and development, and it is crucial to ensure that seeds are given the optimal conditions to sprout and thrive.
Additionally, successful seed germination helps to maintain genetic diversity in plant populations, as it allows for the propagation of different varieties of plants. Ultimately, getting seeds to germinate is key to achieving healthy, productive plants and a bountiful harvest.
The Process of Seeds Germination

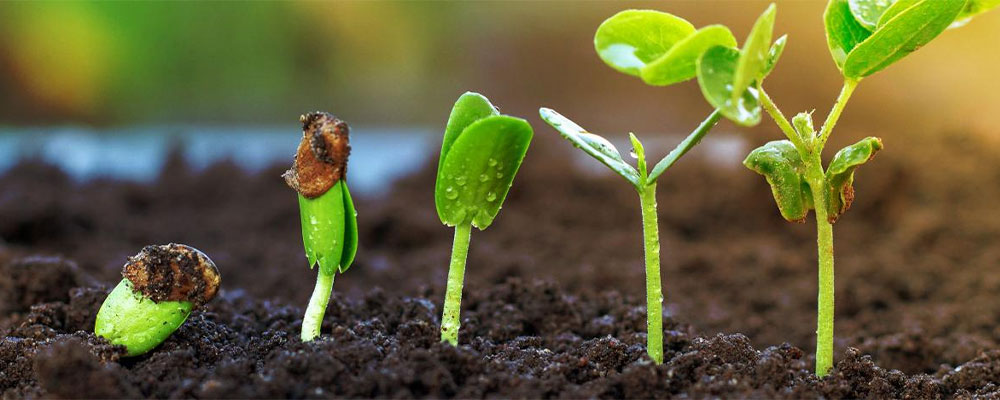
The process of germinating seeds is a complex and highly regulated process that involves the activation of a dormant embryo within the seed, which then grows into a new plant. The process is initiated by a combination of environmental factors, such as water, oxygen, and temperature.
When a seed is exposed to water, it begins to absorb it through small openings in the seed coat called micropyles. This triggers the indoor seed to start the germination process. Water is a critical component for germinating seeds indoors, as it softens the seed coat and activates enzymesthat break down stored food reserves.
As the seed absorbs water, enzymes within the seed are activated, which break down stored food reserves, such as starch and proteins, into simpler compounds that the growing embryo can use. These compounds are transported to the embryo, which then begins to grow. The embryo first develops a root that emerges from the seed, followed by the shoot that grows upward toward the light.
Once the shoot emerges from the garden soil, the young plant can begin photosynthesis, which is the process of converting sunlight into energy. The leaves of the plant use the energy from the sun to produce glucose, which is used to fuel growth. The root system of the plant continues to grow, allowing it to anchor itself in the soil and absorb nutrients and water.
The process of germinating seeds indoors can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the species of plant and the environmental conditions. Some seeds require specific environmental cues, such as cold temperatures or exposure to fire, before they can germinate seeds. Once the plant has established itself and developed a strong root system, it can continue to grow and mature, producing flowers and seeds, and continuing the cycle of growth and reproduction.
Factors that Affect Seeds Germination
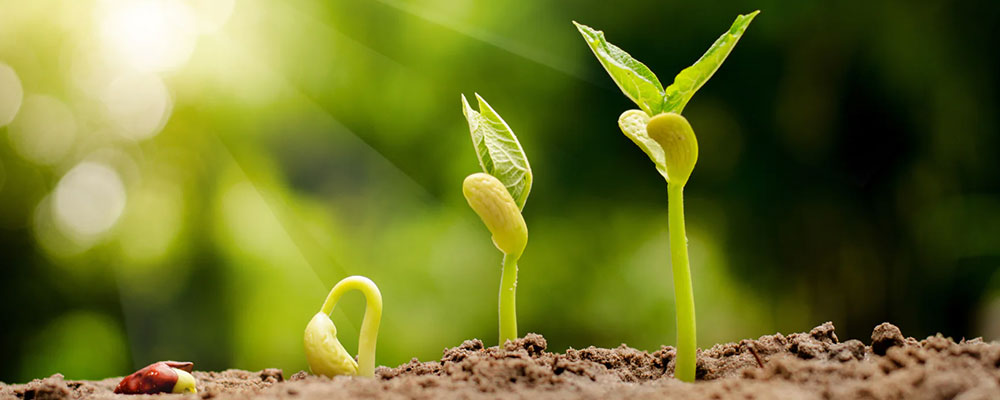

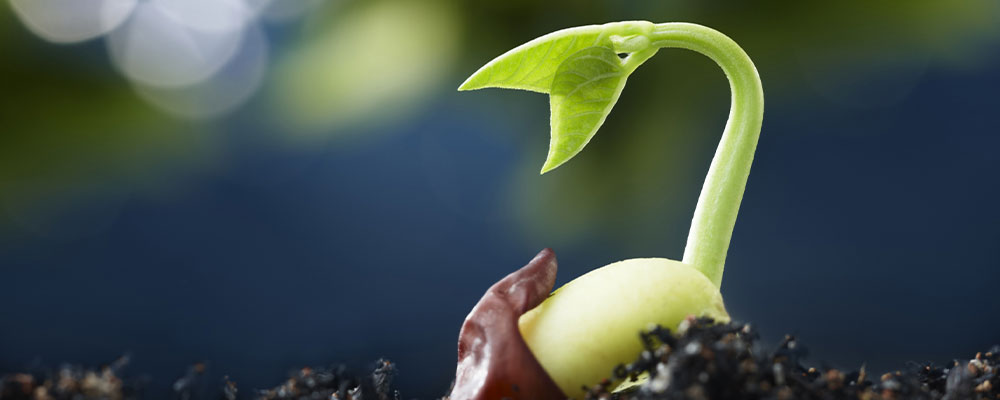
- Temperature
Temperature is one of the most important environmental factors that affect seeds germination. Most seeds indoors have a specific temperature range at which they will germinate, and this range can vary widely between different species of plants. Generally, seeds will not germinate below a certain minimum temperature or above a certain maximum temperature. If the temperature is too low, the metabolic activity of the seed will be slow and it will take longer for the seed to germinate.
On the other hand, if the temperature is too high, the seed may not be able to absorb enough water to begin the germination process or may become damaged due to high heat. In addition to minimum and maximum temperature ranges, many seeds indoors also have an optimal temperature range at which they will germinate most effectively. This range is typically between 15°C to 30°C, depending on the species.
- Water
Water is one of the most critical environmental factors that affect seeds germinate. Seeds indoors require water to break dormancy and initiate the germination process. When water is available, the seed absorbs it through the outer layer, or seed coat, which begins the process of imbibition. As the seed imbibes water, it begins to swell, and the seed coat softens, allowing the embryo to emerge.
The availability of water is also essential for the activation of enzymes that break down stored food in the seed, making it available to the embryo. This process provides the energy required for the seedling to grow and develop until it can photosynthesizeon its own.
However, water availability must be balanced as excess water can cause the seed to drown, leading to rot and death. Inadequate water can lead to dehydration, causing the seed to remain dormant or die. The ideal amount of water required for seeds germinate varies depending on the species, but in general, a seed requires about twice its weight in water to germinate seeds.
- Oxygen
Oxygen is another crucial environmental factor that affects seed germination. During the germination process, the embryo within the seed requires oxygen to carry out cellular respiration, a process that produces energy required for growth and development. Oxygen diffuses through the seed coat and into the embryo, where it is used in cellular respiration to break down stored food, producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate) that fuels seedling growth.
The availability of oxygen is particularly important in the early stages of seeds germinate when the embryo is just beginning to develop. If oxygen is not available, the embryo may not receive enough energy to grow, leading to death. This is why adequate soil aeration is crucial for seed germination. Soil compaction, which reduces soil porosity and air spaces, can limit oxygen availability, negatively impacting seed germination.
- Light
Light is another critical environmental factor that affects seed germination, but its importance varies depending on the species. Some seeds require light to germinate, while others require darkness. Seeds that require light to germinate are known as photoblastic seeds, and those that require darkness are known as photoblastic seeds.
Photoblastic seeds require light to trigger specific biochemical reactions that lead to germination. These seeds have receptors in their seed coats that detect light, which signals the embryo to break dormancy and initiate the germination process. The intensity, duration, and wavelength of light required for germination vary depending on the species. For example, lettuce seeds require only a few hours of light exposure to germinate, while some desert plants require intense sunlight to break dormancy.
On the other hand, photoblastic seeds require darkness to initiate the germination process. These seeds have inhibitory compounds in their seed coats that prevent germination until they are exposed to darkness, which breaks down the inhibitors. Once the inhibitors are broken down, the seed can absorb water and initiate the germination process.
- Soil PH
Soil pH is a measure of the soil’s acidity or alkalinity, with a pH of 7 considered neutral. Most plant species have an optimal pH range in which they can grow and thrive, and the germination of seed is no exception.
Different plant species have varying pH preferences for germination, but in general, most prefer slightly acidic to neutral soils. Seeds that prefer acidic soils have a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5, while those that prefer neutral soils have a pH range of 6.5 to 7.5. Soil pH outside of these ranges can negatively impact seed germination, leading to reduced germination rates and delayed growth.
Highly acidic soils, with a pH below 5.5, can affect seed germination by damaging the seed coat, which can make it difficult for the embryo to emerge. In addition, acidic soils can limit the availability of essential nutrients required for seed germination, such as phosphorus and calcium, which can lead to reduced seedling growth.
On the soil surface on the other hand, highly alkaline soils, with a pH above 7.5, can affect seed germination by inhibiting the breakdown of seed coat inhibitors, leading to delayed germination. In addition, alkaline soils can limit the availability of nutrients, particularly iron, which is essential for seed germination.
In summary, soil pH is a crucial environmental factor that affects the germination of seed. Most plant species prefer slightly acidic to neutral soils for germination, and soil pH outside of these ranges can negatively impact seed germination rates and seedling growth.
What You Can Do to Help the Germination of Your Seeds indoors?
In addition to some force majeure, you can also make some artificial efforts to help your beloved plants germinate. The easiest way is to use some growing equipment that is convenient to buy.
Grow tents can indeed be a useful piece of equipment for promoting the germination and growth of seeds indoors. These indoor tents provide seed packets with a controlled environment that can help seed packets maintain optimal temperature and humidity, consistent moisture levels, and good air circulation around seed packets, which are crucial factors for successful germination of seeds indoors.
Additionally, grow tents can protect seedlings from environmental stressors like pests, wind, and extreme weather conditions, which can inhibit growth or even kill the seedlings.

LED grow lights are another important piece of equipment that can be beneficial for seed germination. These lights provide a full spectrum of light that is ideal for promoting photosynthesis and healthy plant growth. Additionally, LED grow lights are energy-efficient and emit less heat than traditional grow lights, which can be especially important when starting seedlings as excessive heat can cause damage or even kill the delicate plants.
LED grow lights can also be adjustable, allowing you to customize the intensity and duration of light exposure, which can help prevent young seedlings from becoming leggy or stunted. By using LED grow lights in conjunction with other appropriate equipment, such as grow tents and quality soil, you can create the ideal environment for your vegetable seeds to germinate and grow into healthy plants.
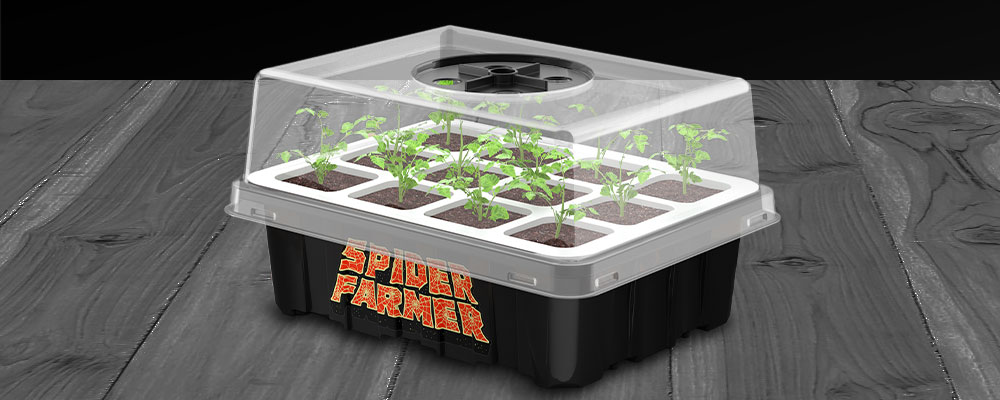

Seed trays are another helpful piece of equipment that can aid in the germination of seeds. These seed trays are designed specifically for starting seeds and provide a compact and controlled environment for the seeds to grow and improve soil moist. Seed trays typically have individual cells that can hold individual seeds, which helps prevent overcrowding and allows for easier transplanting later on. Additionally, seed starting trays are usually made from materials that allow for good drainage and aeration, which can prevent over-watering and promote healthy root growth.

A heat mat is another useful piece of equipment that can aid in the germination of seeds. These mats provide a gentle and consistent source of heat to the soil, which can help speed up the germination process and promote healthy root growth. Heat mats are especially helpful for sprouting seeds that require warmer soil temperatures to germinate, such as peppers, tomatoes, and other warm-season vegetables. Heat mats are easy to use and can be placed underneath seed starting trays or other containers. They are also adjustable, allowing you to control the temperature and prevent overheating or drying out of the soil.

A cool mist humidifier for growing plants is another useful piece of equipment that can aid in the germination of seeds. These humidifiers add moisture to the air, which can help maintain optimal humidity levels for successful seed germination and healthy plant growth. Low humidity can cause seeds to dry out and prevent them from germinating, while high humidity can lead to mold growth and other issues. So a cool mist humidifier for plants can be especially helpful in dry climates or during the winter months when indoor heating can reduce the moisture in the air. These humidifiers are easy to use and can be placed near seed starting trays or other plants. They are also adjustable, allowing you to control the humidity level and prevent over-saturation.
Common Problems Encountered During Seed Germination

Despite the best efforts of even the most experienced gardeners, problems can arise during seed germination. Some common issues encountered during seed germination include:
Poor germination: This can be caused by a number of factors, such as old or low-quality seeds, improper soil temperature or moisture, or insufficient light.
Damping off: This is a fungal disease that causes seedlings to wilt and collapse at the soil level. Damping off is usually caused by overwatering, poor ventilation, or contaminated soil or equipment.
Leggy seedlings: This occurs when seedlings grow tall and thin in search of light, which can be caused by insufficient light or improper spacing.
Mold or mildew: This can be caused by high humidity, poor air circulation, or contaminated soil or equipment.
Seedling transplant shock: This occurs when seedlings are moved to a new location or container and experience stress, which can cause wilting, yellowing, or stunted growth.
Pest damage: Pests like aphids, mites, and slugs can damage or even kill seedlings, causing stunted growth or death.
To avoid these problems, it is important to use high-quality seeds and appropriate equipment, maintain proper soil temperature and moisture, provide adequate light and ventilation, and regularly inspect and clean equipment and soil. Additionally, taking preventative measures such as using organic pest control methods and practicing good hygiene can help prevent issues from arising.
Get Growing Equipment to Help Your Plant Seeds Germination
Growers are looking for ways to help their seeds germinate quickly in this Spring. If you have the same need, now is a great time. To celebrate 420(The Cannabis Culture Day), we have up to 20% discount on our products this month. Please seize this opportunity to choose the best equipment for your seeds, don’t miss it, and look forward to its blooming.























Good article